How to Save Money on AWS: 10 Tips to Consider
Development in the cloud has long proven its efficiency. It allows you to access advanced IT resources on demand and avoid the headache of setting up on-prem IT infrastructure. Cloud computing provides ample opportunities for scaling up as your business evolves and grows. However, it may strain your budget if you don't control cloud service costs and don't develop a clear pricing model.
This post aims to share insights on optimizing the costs of the most popular cloud service provider, AWS. The recommendations are provided based on 11+ years of experience of Erbis engineers with diverse backgrounds and software projects under their belts. Here are ten tips to follow.
Review your bill
Cost reduction starts with cost understanding, so take the time to review your AWS bill to clarify what you're spending your money on and where you can make cuts.
To better understand the nature of your AWS charges, use AWS Cost Explorer. This tool provides a deep dive into your data usage and offers handy filters to group your spendings by source and time interval. A great thing about Cost Explorer is that you can forecast your future spendings and get an idea of what expenses you will incur if you do not change your cloud computing strategy. Additionally, you can view the data graphically and get a handy AWS cost usage report.
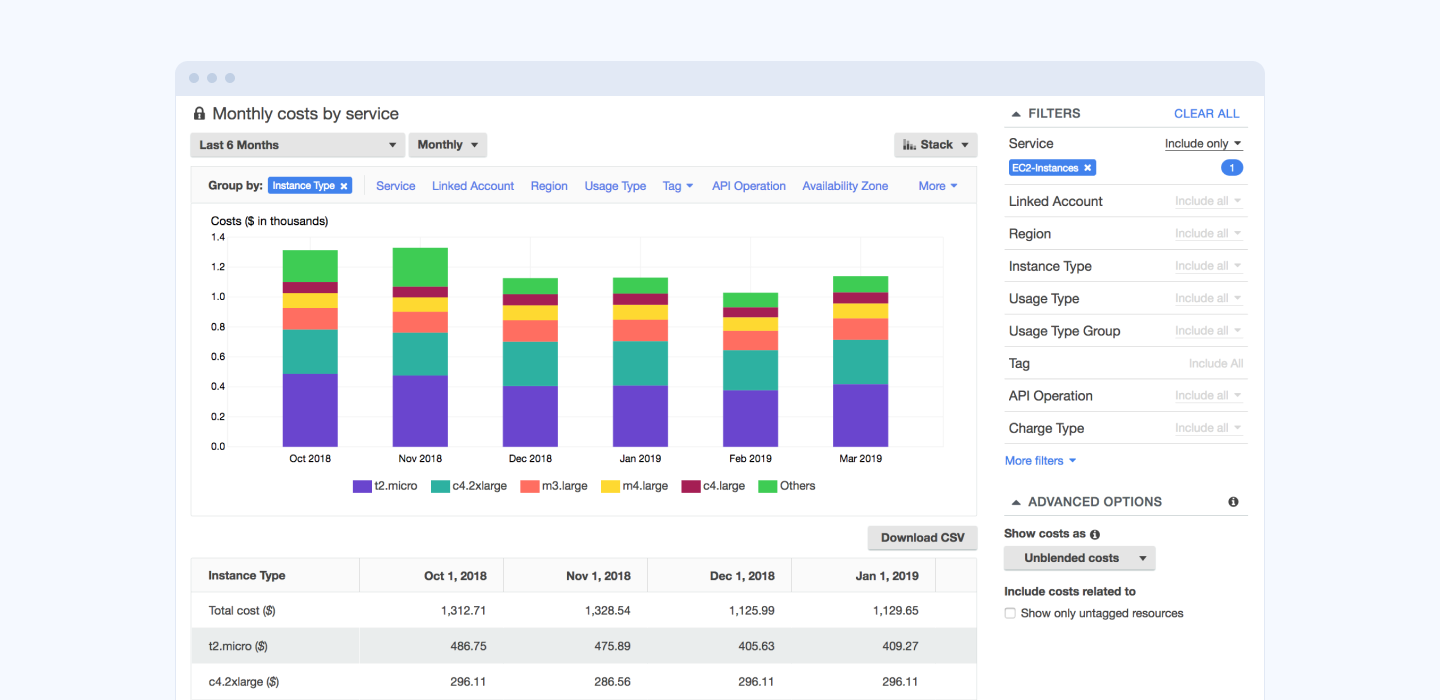
Set up cost alerts
One great way to save money on AWS is to set up cost alerts which will send a notification when your monthly bill reaches a certain amount.
To do this, navigate to the Billing and Cost Management section of the AWS Management Console. Then, click on the Preferences tab and choose the Enable Cost Alerts checkbox.
You can then specify the amount that triggers a notification and the email address where you want to receive the alerts.
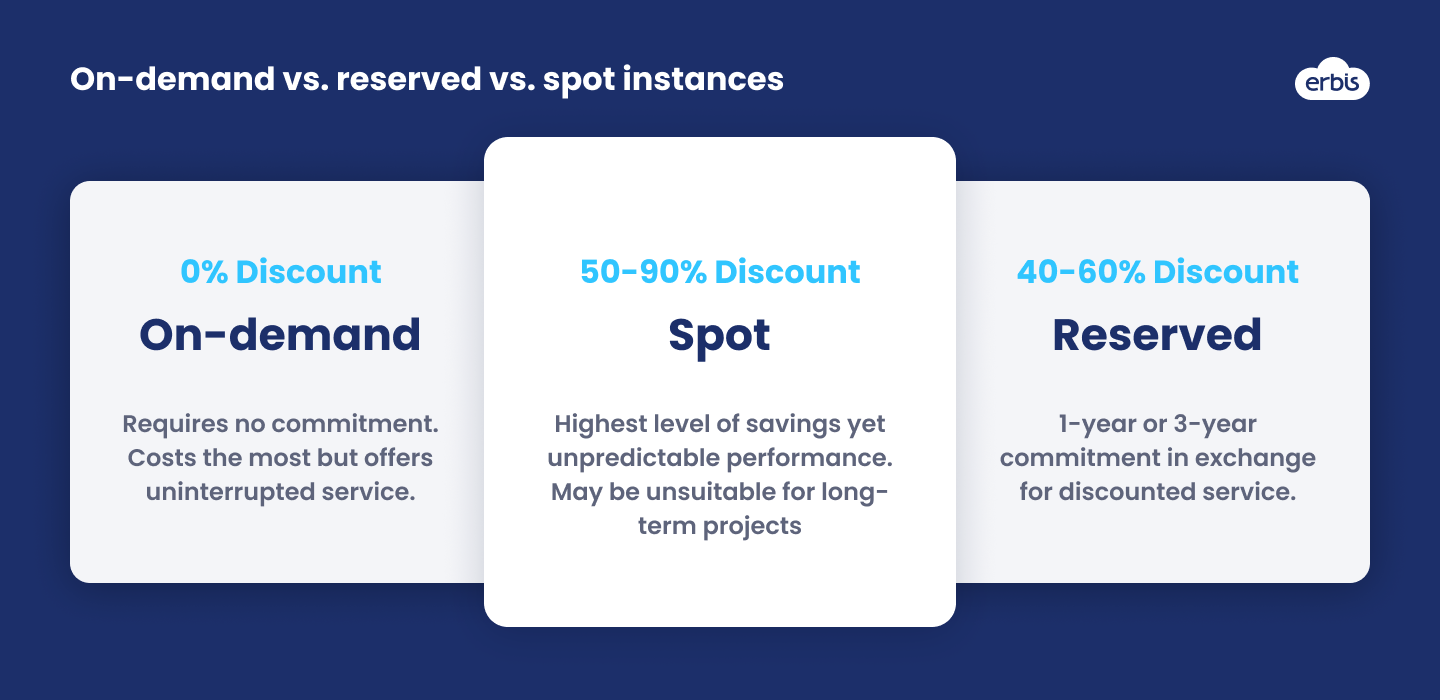
Use reserved instances
You can save significant money on AWS by using reserved instances. With reserved Instances, you make a long-term commitment in return for a significant discount.
But it's important to note that reserved instances are not always the best option. Sometimes it makes more sense to use on-demand instances, especially if your needs are unpredictable or if you use cloud resources only at a specific time.
For example, if you need to rent a virtual machine to run 24/7 for a year or so, a reserved instance would be a perfect choice. However, if you need a virtual machine to work only a few hours a day over a period of several months, it's better to choose an on-demand pricing model.
If you need help figuring out the best option for you, our experts are more than happy to help. We can analyze your usage data and recommend the best way to reduce AWS costs.
Use spot instances
Spot instances are unused AWS instances that can cost up to 90% less than on-demand instances. You can bid on AWS instances, with the price being determined by supply and demand. If there's less demand for an instance, the price goes down. If there's more demand, the price goes up.
The downside of using spot instances is that you cannot reserve them. If someone else requests to use an instance, you will only receive a few minutes warning before being disconnected.
Reserved instances are suitable for processes that are not sensitive to interruptions and downtimes. For example, it's a good idea to deploy your test environment using spot instances but it's a bad idea to run your e-commerce website there.
To start using AWS spot instances, go into your AWS console and click on Spot Instances. From there, you can choose the type of instance you want to bid on, and how long you want it for.
Opt for DynamoDB instead of RDS
In small and mid-sized projects, you can not only reduce costs for cloud storage but get it for free if your cloud capacity requirements fit within the AWS free tier.
However, for larger projects you should seriously approach the choice of AWS database instance and its price. Here are a few tips to help you make the right choice:
Use DynamoDB for high-speed data processing systems (gaming, bidding, CMS). Use RDS for traditional enterprise-level apps (e-commerce, ERP, CRM).
When opting for DynamoDB, use on-demand capacity mode for systems with unpredictable traffic and select provisioned capacity mode when the traffic is known and stable.
When opting for RDS, consider starting with a monthly subscription. When you understand required storage capacity, switch to an AWS on-demand pricing model and pay depending on the database engine you use.
Utilize S3 infrequently accessed storage classes
S3 Standard-Infrequently Accessed (IA) and S3 One Zone-IA classes are designed for data accessed less than once a month.
Such classes are cheaper than the S3 standard storage class, but you do sacrifice some performance. You can access your data more quickly if you use the S3 standard storage class, but you'll pay more for that convenience.
The difference between S3 Standard-IA and S3 One Zone-IA is that the former stores objects across multiple availability zones, while the latter provides only one availability zone. Also, S3 One Zone-IA does not protect data in case of disasters, but it offers a 20% lower price compared to S3 Standard-IA.
Use CloudFront
CloudFront is a content delivery network (CDN) that caches your web content and delivers it to users from the nearest point of presence. This means that your users will get your content faster, you'll pay less for bandwidth, and reduce your AWS costs.
CloudFront is easy to set up, and you can use it with any of your AWS services. You can also use it to cache objects that are stored in Amazon S3. To get started, create a CloudFront distribution and specify the origin of your content.
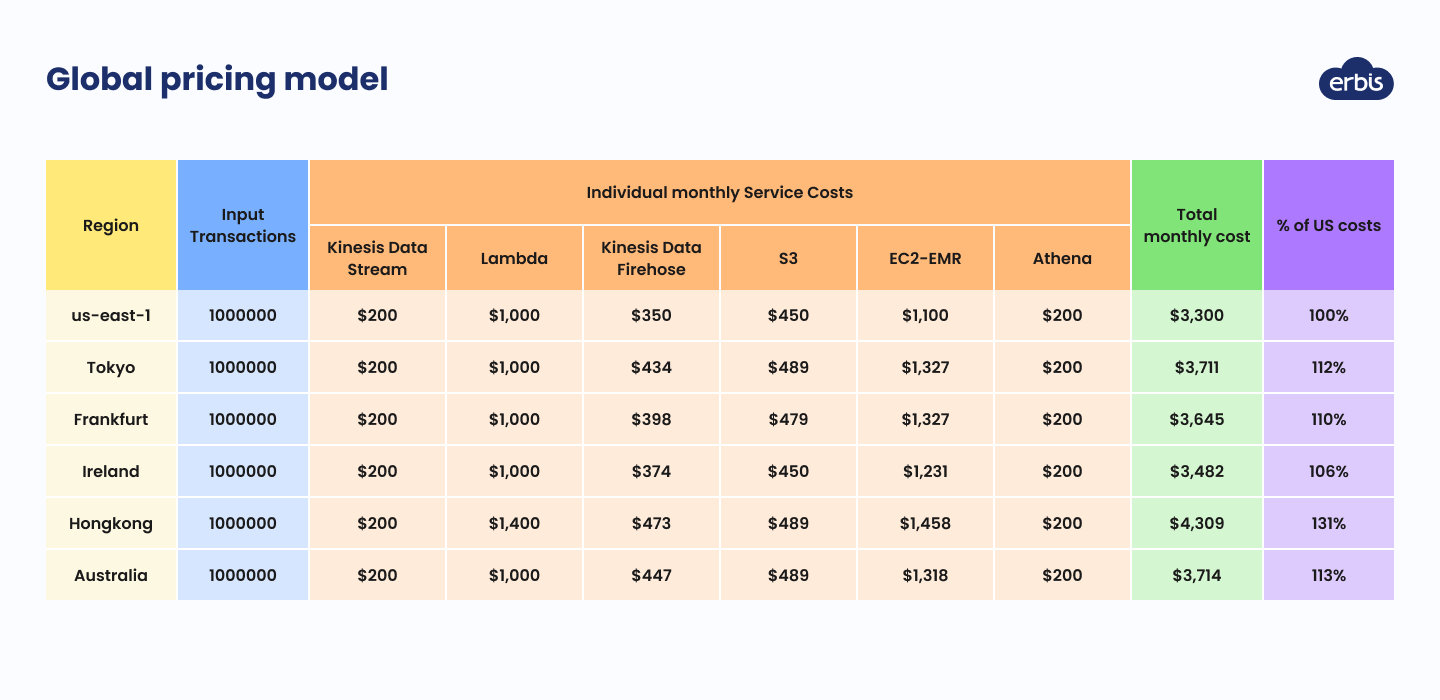
Review instances in different locations
The cost of AWS server maintenance depends on its location. Countries that have fewer taxes, and lower electricity, fiber, and land costs benefit from lower Amazon fees. So, if you are looking for ways to optimize cloud costs, consider reviewing EC2 instance prices for the US, Europe, Asia, and other regions. Before making a final decision, understand how particular AWS services are priced and whether they fit your project needs.
Set up auto scaling
Auto scaling automatically adds or removes cloud computing resources according to your product needs. This is very convenient since you do not have to constantly monitor customers' traffic and you do not risk paying for resources that you do not use and need.
In addition to the automatic adjustment of computing power, Amazon also offers scaling recommendations and predictive scaling plans. This allows you to calculate likely AWS costs in advance and set up a project budget according to your company's goals and opportunities.
Terminate sessions
Each project has processes that run according to a specific schedule and take relatively little time. A good example is report generation.
Let's say you generate reports from 1 to 4 AM. To reduce AWS costs, start your session at 00:50 and terminate it at 4:10. Note that you will be charged for the use of a whole hour if you have used cloud resources for more than 15 minutes.
Summing up
AWS is a leading provider in the cloud computing market. It provides developers with advanced IT resources and covers the needs of any project from enterprise to startup. Companies that use Amazon services benefit from product scalability, business process flexibility, and collaboration efficiency.
However, using AWS may blow your budget unless you use these cost-saving tricks and price optimization strategies.
If you want to cut AWS cloud computing pricing, start with the tips above. If you need a more personalized savings plan, get in touch. Our Cloud Engineers will be happy to consult you on how best to utilize AWS to maximize profit for your project.